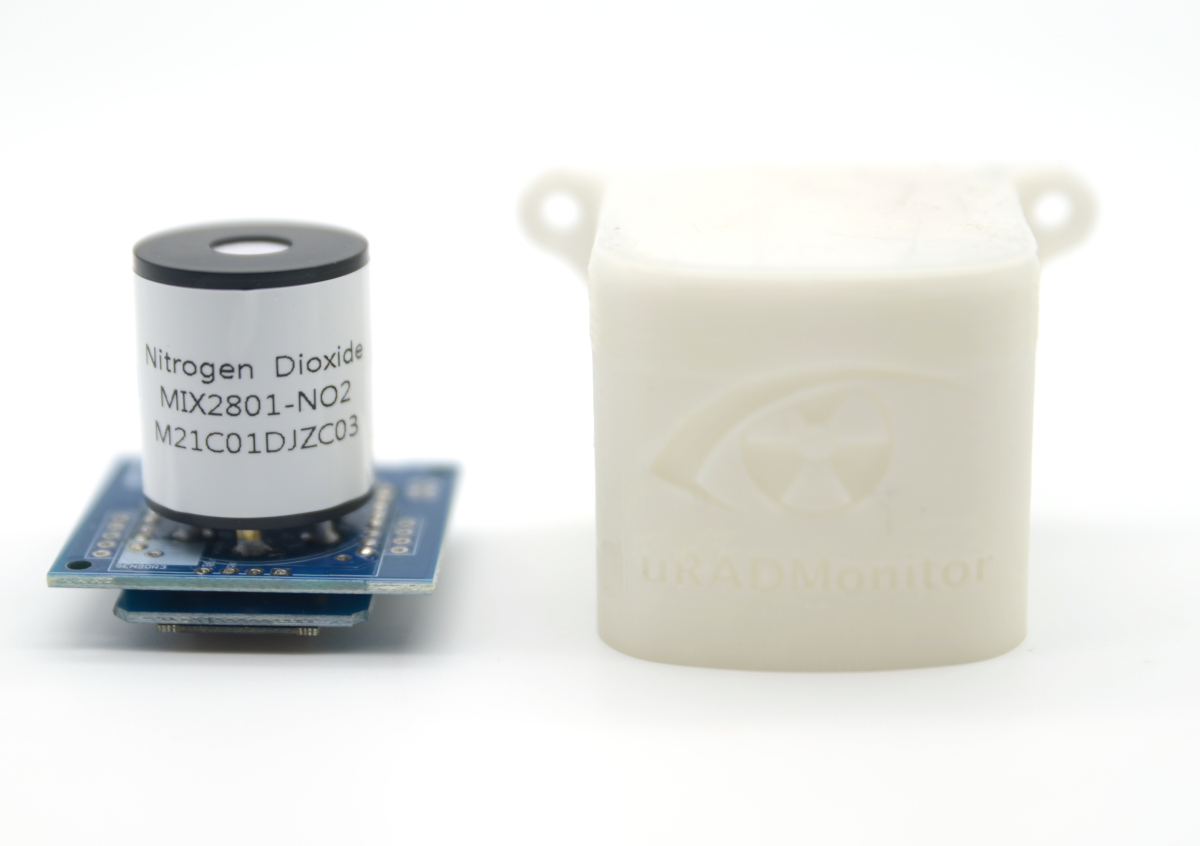
MODEL INDUSTRIALContact us
An automated, fixed monitoring station that tracks a total of 11 important air quality parameters including Particulate Matter, Carbon Monoxide, Ozone, Sulphur Dioxide, Nitrogen Dioxide and more for the INDUSTRIAL sector. It comes in a rugged aluminum enclosure with wall mounting support. The data is exported to the uRADMonitor network with Wifi or LORAWAN, and can be accessed in real time using the cloud API interface or directly via the local network.
Marek, Slovakia: "Wish you good luck with your great work."
uRADMonitor model INDUSTRIAL uses a high quality laser scattering sensor to measure Particulate Matter PM1, PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations in air. Four additional electrochemical sensors measure Carbon Monoxide, Sulphur Dioxide, Nitrogen Dioxide and Ozone by default, interchangeable to support additional gases resulting from production or industrial processes. A MOX VOC sensor measures volatile organic compounds. A built in fan assures an active air flow stream across the sensing elements. The MEMs sensor reads ambient temperature and humidity, and a noise sensor measures the noise level. This product is intended for the industrial sector where medium and high gas concentrations need to be observed.
By the nature of the technology used, any sensor can potentially fail to meet specification without warning. We make every effort to ensure reliability of all sensors but where life safety is a performance requirement of the product and, where practical, we recommend that all gas sensors and instruments using sensors are checked for response to gas before use.
We accept no liability for any consequential losses, injury or damage resulting from the use of the uRADMonitor products. Customers should test the sensors under their own conditions to ensure that the sensors are suitable for their own requirements and in accordance with the plans and circumstances of the specified project and any standards / regulations pertaining to the country in which the sensors will be utilized.
Notes:
Only sensors marked in green are currently available.
All sensors are individually tested and calibrated.
| Sensor | Parameter | Minimum value | Maximum value |
| MEMs | Temperature | -40 °C | +85 °C |
| Humidity | 0% RH | 100% RH | |
| Laser scattering | PM1.0 | 0 μg/m³ | 1000 μg/m³ |
| PM2.5 | 0 μg/m³ | 1000 μg/m³ | |
| PM10 | 0 μg/m³ | 1000 μg/m³ | |
| MOX | VOC | 10 ppm | 1000 ppm * |
| Analogue sound sensor | Noise level | 30dB | 130dB |
| Electrochemical | Ozone | 0 ppm | 10 ppm |
| Electrochemical | Nitrogen Dioxide | 0 ppm | 10 ppm |
| Electrochemical | Sulphur Dioxide | 0 ppm | 20 ppm |
| Electrochemical | Carbon Monoxide | 0 ppm | 200 ppm |
Custom gases detection options
* The unit comes with Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulphur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide calibrated electrochemical sensors built in. These 4 sensors, can be replaced with any combination of sensors for the below gases and ranges. In some situations we can offer custom detection intervals (eg. 0-1000ppm for CO, etc):| Symbol | Gas | Detection interval |
| CO | Carbon monoxide | 0 - 200ppm |
| O2 | Oxigen | 0 - 25%VOL |
| NH3 | Ammonia gas | 0 - 100ppm |
| H2S | Hydrogen sulfide | 0 - 100ppm |
| SO2 | Sulfur dioxide | 0 - 20ppm |
| NO2 | Nitrogen dioxide | 0 - 10ppm |
| Cl2 | Chlorine gas | 0 - 20ppm |
| O3 | Ozone | 0 - 10ppm |
| H2 | Hydrogen gas | 0 - 1000ppm |
| HF | Hydrogen fluoride | 0 - 10ppm |
| C2H4 | Ethylene | 0 - 100ppm |
| CH2O | Formaldehyde | 0 - 10ppm |
| ETO | Ethylene oxide | 0 - 20ppm |
| HCl | Hydrogen chloride | 0 - 20ppm |
| C6H6 | Benzene | 0 - 100ppm |
| C7H8 | Toluene | 0 - 500ppm |
| C2H3Cl | Vinyl chloride | 0 - 20ppm |
| C2H6S | Methyl Sulfide | 0 - 100ppm |
| C2H6S2 | Dimethyl Disulfide | 0 - 100ppm |
| AsH3 | Arsine | 0 - 3ppm |
| C3H9N | Trimethylamine | 0 - 100ppm |
| C8H8 | Styrene | 0 - 100ppm |
| CH4S | Methanethiol | 0 - 100ppm |
| CS2 | Carbon Disulfide | 0 - 100ppm |
| PH3 | Phosphine | 0 - 10ppm |
| HCN | Hydrogen cyanide | 0 - 100ppm |
Air pollution is the single largest environmental cause of premature death in urban Europe and transport is the main source. The 2008 Air Quality Directive, now under review, obliges member states to cut exposure to fine particulate matter by an average of 20% by 2020, based on 2010 levels.
The National Emissions Ceiling Directive caps some emissions including particulate matter (PM) and nitrogen dioxide (NOx) at national level. A revised version of the directive is as of 2016 under scrutiny by the Council of Ministers and European Parliament. Across the EU in 2013, nitrogen dioxide (NO2), which is mostly produced by traffic, caused 68,000 premature deaths. The Dieselgate scandal exposed how Volkswagen had gamed NO2 emissions tests.
Ozone (O3) killed 16,000 and small particulate matter (PM2.5) caused 436,000 deaths in the same year. PM2.5 particles, microscopic specks of dust and soot caused by burning fossil fuels, can enter the lungs and bloodstream.
 Air pollution has different particulate matter (PM) components – smoke, dirt and dust form coarse particles known as PM10 and metals and toxic exhaust from smelting, vehicle exhaust, power plants and refuse burning forming fine particles called PM2.5.
Air pollution has different particulate matter (PM) components – smoke, dirt and dust form coarse particles known as PM10 and metals and toxic exhaust from smelting, vehicle exhaust, power plants and refuse burning forming fine particles called PM2.5.
uRADMonitor INDUSTRIAL is intended for the industrial sector where medium and high gas concentrations need to be observed.
The National Emissions Ceiling Directive caps some emissions including particulate matter (PM) and nitrogen dioxide (NOx) at national level. A revised version of the directive is as of 2016 under scrutiny by the Council of Ministers and European Parliament. Across the EU in 2013, nitrogen dioxide (NO2), which is mostly produced by traffic, caused 68,000 premature deaths. The Dieselgate scandal exposed how Volkswagen had gamed NO2 emissions tests.
Ozone (O3) killed 16,000 and small particulate matter (PM2.5) caused 436,000 deaths in the same year. PM2.5 particles, microscopic specks of dust and soot caused by burning fossil fuels, can enter the lungs and bloodstream.
 Air pollution has different particulate matter (PM) components – smoke, dirt and dust form coarse particles known as PM10 and metals and toxic exhaust from smelting, vehicle exhaust, power plants and refuse burning forming fine particles called PM2.5.
Air pollution has different particulate matter (PM) components – smoke, dirt and dust form coarse particles known as PM10 and metals and toxic exhaust from smelting, vehicle exhaust, power plants and refuse burning forming fine particles called PM2.5.uRADMonitor INDUSTRIAL is intended for the industrial sector where medium and high gas concentrations need to be observed.
The model INDUSTRIAL is designed as a fixed monitoring station. It comes in 2 variants, with the same sensors but offering different connectivity options: Wifi and LoraWAN. It takes any voltage in the 6V - 24V interval and uses less than 1 Watt of power to run. It can be powered using a small solar panel making it the perfect remote surveillance monitor. This unit doesn't have a screen, it works as a monitor and the data can be viewed remotely on a computer or on a mobile device.
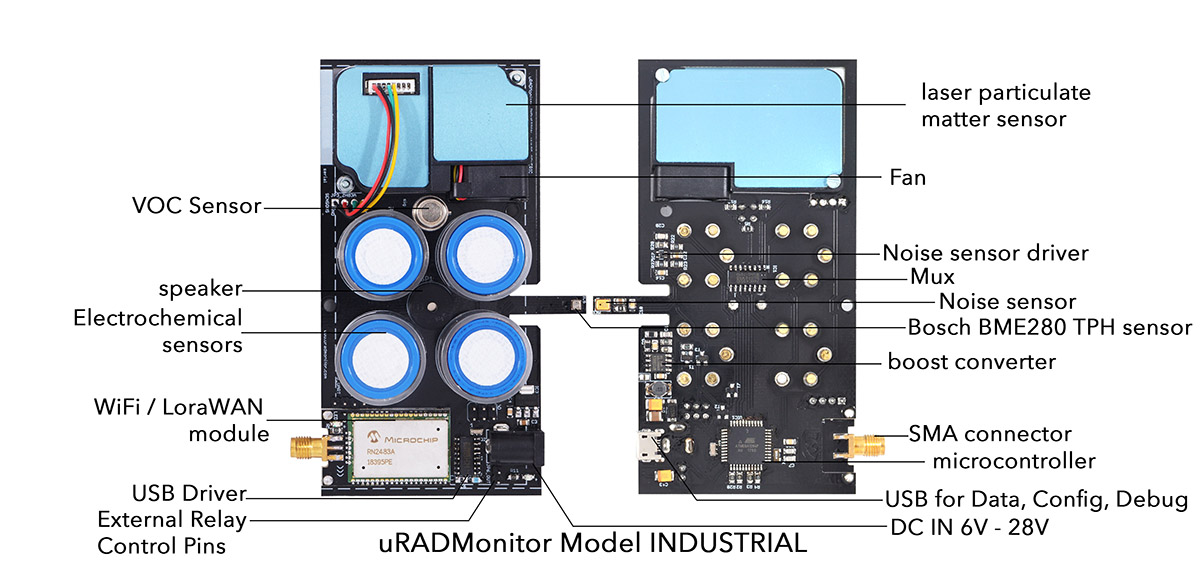
Picture: uRADMonitor INDUSTRIAL motherboard front and bottom view

| Item | Parameter | Ratings |
| Voltage | External | 6V - 24V |
| Connectivity | 4 options | WiFi, LoRaWAN, USB |
| Microcontroller | Atmega1284p | 8 bit |
Your uRADMonitor unit can be mounted both indoors and outdoors, but not directly exposed to sun, to avoid overheating in warmer areas. A covered spot with some shadow if installed in the free air, is ideal. The unit has a rugged aluminium enclosure that is not rainproof due to the air vents. Make sure that nothing is blocking the air vents. The enclosure has wall-mounting brackets, making installation easy.
If you have a radio variant with an antenna, connect the antenna first. Next, connect the uRADMonitor to the power source using a DC adapter with voltage between 6V and 24V. Connect the uRADMonitor to the power source using a DC adapter with voltage between 6V and 24V or via the USB port with a 5V USB adapter.
The WIFI variant
Use a smartphone or a computer with WLAN capabilities to connect to the local hotspot spawned by your unit. The SSID is uRADMonitor-XX, where XX are the last two digits of the Device ID number. The key is the Device ID, in uppercase, as printed on the enclosure. Open 192.168.4.1 in your browser, and click the "WIFI" link to setup the connection to the Internet AP. Enter the SSID and key of your Internet Access Point. If the connection fails, you will see the status message, and three consecutive beeps will indicated the problem. Alternatively you can change the configuration using the USB data port. See the USB manual.
The LORAWAN variant
Your device must be pre-provisioned with the LoraWAN Gateway and network server details. Alternativelly you can change the configuration using the USB data port. See the USB manual.
The device comes with an USB port, so the configuration settings can be customized via the USB connection. Consult your product manual for complete details.
If you have a radio variant with an antenna, connect the antenna first. Next, connect the uRADMonitor to the power source using a DC adapter with voltage between 6V and 24V. Connect the uRADMonitor to the power source using a DC adapter with voltage between 6V and 24V or via the USB port with a 5V USB adapter.
The WIFI variant
Use a smartphone or a computer with WLAN capabilities to connect to the local hotspot spawned by your unit. The SSID is uRADMonitor-XX, where XX are the last two digits of the Device ID number. The key is the Device ID, in uppercase, as printed on the enclosure. Open 192.168.4.1 in your browser, and click the "WIFI" link to setup the connection to the Internet AP. Enter the SSID and key of your Internet Access Point. If the connection fails, you will see the status message, and three consecutive beeps will indicated the problem. Alternatively you can change the configuration using the USB data port. See the USB manual.
The LORAWAN variant
Your device must be pre-provisioned with the LoraWAN Gateway and network server details. Alternativelly you can change the configuration using the USB data port. See the USB manual.
The device comes with an USB port, so the configuration settings can be customized via the USB connection. Consult your product manual for complete details.
Quick Start
Technical Datasheet
USB Serial Commands Manual
LoRaWAN Data Server Callback manual
Product Limited Warranty terms
uRADMonitor with WIFI Configuration manual
Data access:
Terms of Service
API Terms of Service
API and Server Specs
Direct Data access
Payload Structure (FW78)
USB Driver
In their recent versions, Windows, Linux and MacOS come with built in drivers for your uRADMonitor unit. Use the following resources only if the built in drivers do not work for you.
USB Driver for Windows
USB Driver for Linux
USB Driver for MacOS
RO:
Fisa tehnica
Technical Datasheet
USB Serial Commands Manual
LoRaWAN Data Server Callback manual
Product Limited Warranty terms
uRADMonitor with WIFI Configuration manual
Data access:
Terms of Service
API Terms of Service
API and Server Specs
Direct Data access
Payload Structure (FW78)
USB Driver
In their recent versions, Windows, Linux and MacOS come with built in drivers for your uRADMonitor unit. Use the following resources only if the built in drivers do not work for you.
USB Driver for Windows
USB Driver for Linux
USB Driver for MacOS
RO:
Fisa tehnica
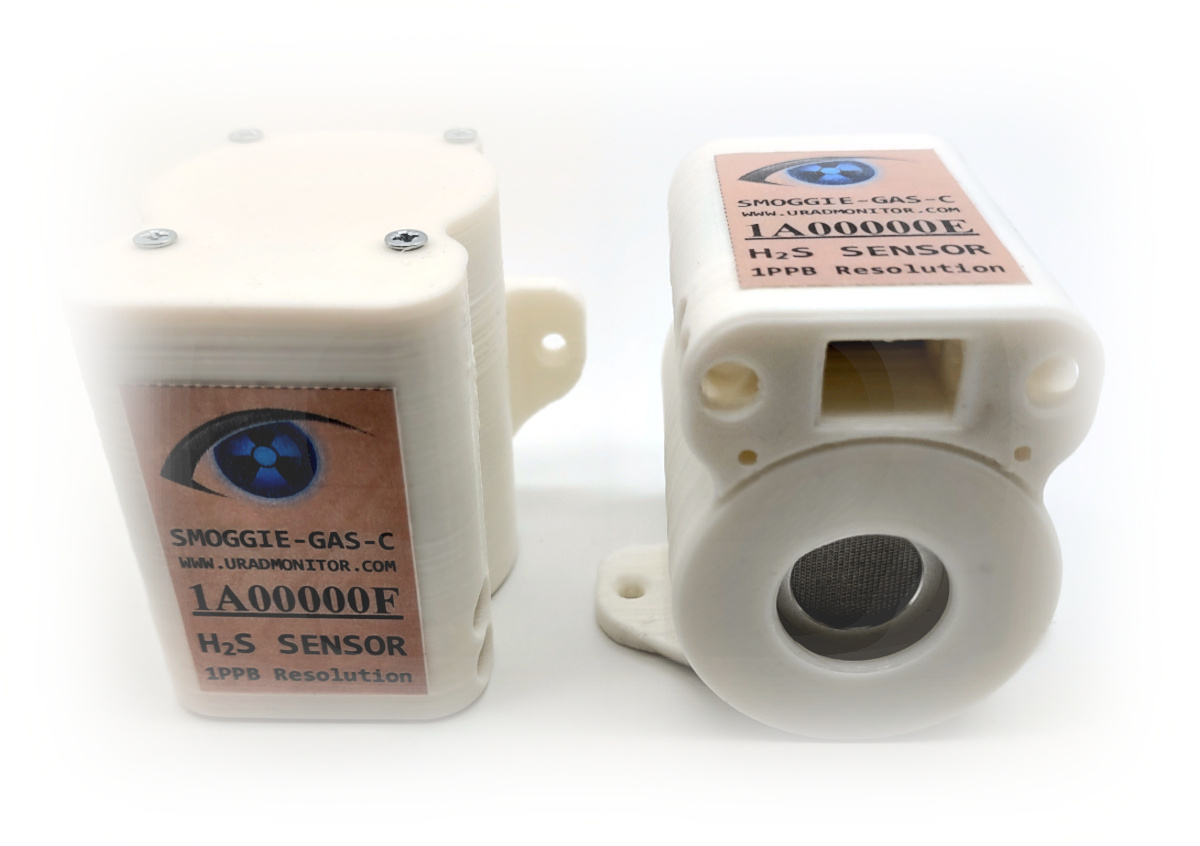
SMOGGIE-GASContact us
This is a compact, automated GAS monitor. It accommodates a single electrochemical cell that you can choose to match the gas you need to detect. Currently we support H2S, CO, O2, NH3, NO2, HF, SO2, CL2, O3, H2, HCL. There is an additional sensor for temperature and humidity. It connects to the internet via Wifi and can be powered by a standard 5V micro-usb cable. It provides real time 24/7 monitoring for toxic gases.
Swaleh, Mauritius: "You have a good vision for the wellness of mankind, your effort will pay and mankind will benefit."
SMOGGIE-GAS is an automated, fixed, toxic gases monitoring station. It has Wifi connectivity to send the air quality measurements to the uRADMonitor Cloud in real time. It needs 5V to run, powered by a standard micro-USB cable. This unit doesn't have a screen, it works as a monitor and the data can be viewed remotely on a computer or on a mobile device.
To see complete specs see the technical datasheet.
By the nature of the technology used, any sensor can potentially fail to meet specification without warning. We make every effort to ensure reliability of all sensors but where life safety is a performance requirement of the product and, where practical, we recommend that all gas sensors and instruments using sensors are checked for response to gas before use. We accept no liability for any consequential losses, injury or damage resulting from the use of the uRADMonitor products. Customers should test the sensors under their own conditions to ensure that the sensors are suitable for their own requirements and in accordance with the plans and circumstances of the specified project and any standards / regulations pertaining to the country in which the sensors will be utilized.
| Sensor | Parameter | Resolution | Minimum value | Maximum value |
| MEMs | Temperature | 0.5°C | -40 °C | +85 °C |
| Humidity | 1%RH | 0%RH | 100% RH | |
| Electrochemical Sensor | H2S | 0.1 ppm | 0 ppm | 100 ppm |
| O3 | 0.1 ppm | 0 ppm | 10 ppm | |
| NO2 | 0.1 ppm | 0 ppm | 10 ppm | |
| SO2 | 0.1 ppm | 0 ppm | 20 ppm | |
| CO | 1 ppm | 0 ppm | 200 ppm |
By the nature of the technology used, any sensor can potentially fail to meet specification without warning. We make every effort to ensure reliability of all sensors but where life safety is a performance requirement of the product and, where practical, we recommend that all gas sensors and instruments using sensors are checked for response to gas before use. We accept no liability for any consequential losses, injury or damage resulting from the use of the uRADMonitor products. Customers should test the sensors under their own conditions to ensure that the sensors are suitable for their own requirements and in accordance with the plans and circumstances of the specified project and any standards / regulations pertaining to the country in which the sensors will be utilized.
Hydrogen sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula H2S. It is a colorless chalcogen hydride gas with the characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. It is very poisonous, corrosive, and flammable.
Hydrogen sulfide is often produced from the microbial breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen gas, such as in swamps and sewers; this process is commonly known as anaerobic digestion which is done by sulfate-reducing microorganisms. H2S also occurs in volcanic gases, natural gas, and in some sources of well water. [1]
Hydrogen sulfide is a broad-spectrum poison, meaning that it can poison several different systems in the body, although the nervous system is most affected. The toxicity of H2S is comparable with that of carbon monoxide. It binds with iron in the mitochondrial cytochrome enzymes, thus preventing cellular respiration. Since hydrogen sulfide occurs naturally in the body, the environment, and the gut, enzymes exist to detoxify it. At some threshold level, believed to average around 300–350 ppm, the oxidative enzymes become overwhelmed. Many personal safety gas detectors, such as those used by utility, sewage and petrochemical workers, are set to alarm at as low as 5 to 10 ppm and to go into high alarm at 15 ppm. Detoxification is effected by oxidation to sulfate, which is harmless. Hence, low levels of hydrogen sulfide may be tolerated indefinitely.
Exposure to lower concentrations can result in eye irritation, a sore throat and cough, nausea, shortness of breath, and fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema). These effects are believed to be due to the fact that hydrogen sulfide combines with alkali present in moist surface tissues to form sodium sulfide, a caustic. These symptoms usually go away in a few weeks.
Long-term, low-level exposure may result in fatigue, loss of appetite, headaches, irritability, poor memory, and dizziness. Chronic exposure to low level H2S (around 2 ppm) has been implicated in increased miscarriage and reproductive health issues among Russian and Finnish wood pulp workers, but the reports have not (as of circa 1995) been replicated.
Short-term, high-level exposure can induce immediate collapse, with loss of breathing and a high probability of death. If death does not occur, high exposure to hydrogen sulfide can lead to cortical pseudolaminar necrosis, degeneration of the basal ganglia and cerebral edema. Although respiratory paralysis may be immediate, it can also be delayed up to 72 hours.
0.00047 ppm or 0.47 ppb is the odor threshold, the point at which 50% of a human panel can detect the presence of an odor without being able to identify it.
10 ppm is the OSHA permissible exposure limit (PEL) (8 hour time-weighted average).
10–20 ppm is the borderline concentration for eye irritation.
20 ppm is the acceptable ceiling concentration established by OSHA.
50 ppm is the acceptable maximum peak above the ceiling concentration for an 8-hour shift, with a maximum duration of 10 minutes.
50–100 ppm leads to eye damage.
At 100–150 ppm the olfactory nerve is paralyzed after a few inhalations, and the sense of smell disappears, often together with awareness of danger.
320–530 ppm leads to pulmonary edema with the possibility of death.
530–1000 ppm causes strong stimulation of the central nervous system and rapid breathing, leading to loss of breathing.
800 ppm is the lethal concentration for 50% of humans for 5 minutes' exposure (LC50)
Concentrations over 1000 ppm cause immediate collapse with loss of breathing, even after inhalation of a single breath.
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. It is toxic to animals that use hemoglobin as an oxygen carrier (both Invertebrate and vertebrate) when encountered in concentrations above about 35 ppm, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal biological functions. In the atmosphere, it is spatially variable and short lived, having a role in the formation of ground-level ozone.[2] Carbon monoxide poisoning is the most common type of fatal air poisoning in many countries. Carbon monoxide is colorless, odorless, and tasteless, but highly toxic. It combines with hemoglobin to produce carboxyhemoglobin, which usurps the space in hemoglobin that normally carries oxygen, but is ineffective for delivering oxygen to bodily tissues. Concentrations as low as 667 ppm may cause up to 50% of the body's hemoglobin to convert to carboxyhemoglobin. A level of 50% carboxyhemoglobin may result in seizure, coma, and fatality. In the United States, the OSHA limits long-term workplace exposure levels above 50 ppm.
The most common symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning may resemble other types of poisonings and infections, including symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, fatigue, and a feeling of weakness. Affected families often believe they are victims of food poisoning. Infants may be irritable and feed poorly. Neurological signs include confusion, disorientation, visual disturbance, syncope (fainting), and seizures.
Some descriptions of carbon monoxide poisoning include retinal hemorrhages, and an abnormal cherry-red blood hue. In most clinical diagnoses these signs are seldom noticed. One difficulty with the usefulness of this cherry-red effect is that it corrects, or masks, what would otherwise be an unhealthy appearance, since the chief effect of removing deoxygenated hemoglobin is to make an asphyxiated person appear more normal, or a dead person appear more lifelike, similar to the effect of red colorants in embalming fluid. The "false" or unphysiologic red-coloring effect in anoxic CO-poisoned tissue is related to the meat-coloring commercial use of carbon monoxide, discussed below.
Carbon monoxide also binds to other molecules such as myoglobin and mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase. Exposures to carbon monoxide may cause significant damage to the heart and central nervous system, especially to the globus pallidus, often with long-term chronic pathological conditions. Carbon monoxide may have severe adverse effects on the fetus of a pregnant woman.
[1] Hydrogen sulfide
[2] Carbon monoxide
Hydrogen sulfide is often produced from the microbial breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen gas, such as in swamps and sewers; this process is commonly known as anaerobic digestion which is done by sulfate-reducing microorganisms. H2S also occurs in volcanic gases, natural gas, and in some sources of well water. [1]
Hydrogen sulfide is a broad-spectrum poison, meaning that it can poison several different systems in the body, although the nervous system is most affected. The toxicity of H2S is comparable with that of carbon monoxide. It binds with iron in the mitochondrial cytochrome enzymes, thus preventing cellular respiration. Since hydrogen sulfide occurs naturally in the body, the environment, and the gut, enzymes exist to detoxify it. At some threshold level, believed to average around 300–350 ppm, the oxidative enzymes become overwhelmed. Many personal safety gas detectors, such as those used by utility, sewage and petrochemical workers, are set to alarm at as low as 5 to 10 ppm and to go into high alarm at 15 ppm. Detoxification is effected by oxidation to sulfate, which is harmless. Hence, low levels of hydrogen sulfide may be tolerated indefinitely.
Exposure to lower concentrations can result in eye irritation, a sore throat and cough, nausea, shortness of breath, and fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema). These effects are believed to be due to the fact that hydrogen sulfide combines with alkali present in moist surface tissues to form sodium sulfide, a caustic. These symptoms usually go away in a few weeks.
Long-term, low-level exposure may result in fatigue, loss of appetite, headaches, irritability, poor memory, and dizziness. Chronic exposure to low level H2S (around 2 ppm) has been implicated in increased miscarriage and reproductive health issues among Russian and Finnish wood pulp workers, but the reports have not (as of circa 1995) been replicated.
Short-term, high-level exposure can induce immediate collapse, with loss of breathing and a high probability of death. If death does not occur, high exposure to hydrogen sulfide can lead to cortical pseudolaminar necrosis, degeneration of the basal ganglia and cerebral edema. Although respiratory paralysis may be immediate, it can also be delayed up to 72 hours.
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. It is toxic to animals that use hemoglobin as an oxygen carrier (both Invertebrate and vertebrate) when encountered in concentrations above about 35 ppm, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal biological functions. In the atmosphere, it is spatially variable and short lived, having a role in the formation of ground-level ozone.[2] Carbon monoxide poisoning is the most common type of fatal air poisoning in many countries. Carbon monoxide is colorless, odorless, and tasteless, but highly toxic. It combines with hemoglobin to produce carboxyhemoglobin, which usurps the space in hemoglobin that normally carries oxygen, but is ineffective for delivering oxygen to bodily tissues. Concentrations as low as 667 ppm may cause up to 50% of the body's hemoglobin to convert to carboxyhemoglobin. A level of 50% carboxyhemoglobin may result in seizure, coma, and fatality. In the United States, the OSHA limits long-term workplace exposure levels above 50 ppm.
The most common symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning may resemble other types of poisonings and infections, including symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, fatigue, and a feeling of weakness. Affected families often believe they are victims of food poisoning. Infants may be irritable and feed poorly. Neurological signs include confusion, disorientation, visual disturbance, syncope (fainting), and seizures.
Some descriptions of carbon monoxide poisoning include retinal hemorrhages, and an abnormal cherry-red blood hue. In most clinical diagnoses these signs are seldom noticed. One difficulty with the usefulness of this cherry-red effect is that it corrects, or masks, what would otherwise be an unhealthy appearance, since the chief effect of removing deoxygenated hemoglobin is to make an asphyxiated person appear more normal, or a dead person appear more lifelike, similar to the effect of red colorants in embalming fluid. The "false" or unphysiologic red-coloring effect in anoxic CO-poisoned tissue is related to the meat-coloring commercial use of carbon monoxide, discussed below.
Carbon monoxide also binds to other molecules such as myoglobin and mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase. Exposures to carbon monoxide may cause significant damage to the heart and central nervous system, especially to the globus pallidus, often with long-term chronic pathological conditions. Carbon monoxide may have severe adverse effects on the fetus of a pregnant woman.
[1] Hydrogen sulfide
[2] Carbon monoxide
SMOGGIE-GAS is designed as an automated, fixed, Air Quality monitoring station that measures and reports the target gas concentration automatically, 24/7. It comes with built-in Wifi connectivity and it only needs 5V to run, supplied via a standard micro-USB cable. It will monitor your location 24/7 to inform you on elevated GAS levels that can impact your health. Each SMOGGIE-GAS comes with one electrochemical sensor to measure H2S, O3, NO2, SO2 or CO. You can choose the gas at checkout.
The units can be managed via the dashboard. The data can be viewed remotely on a computer or on a mobile device.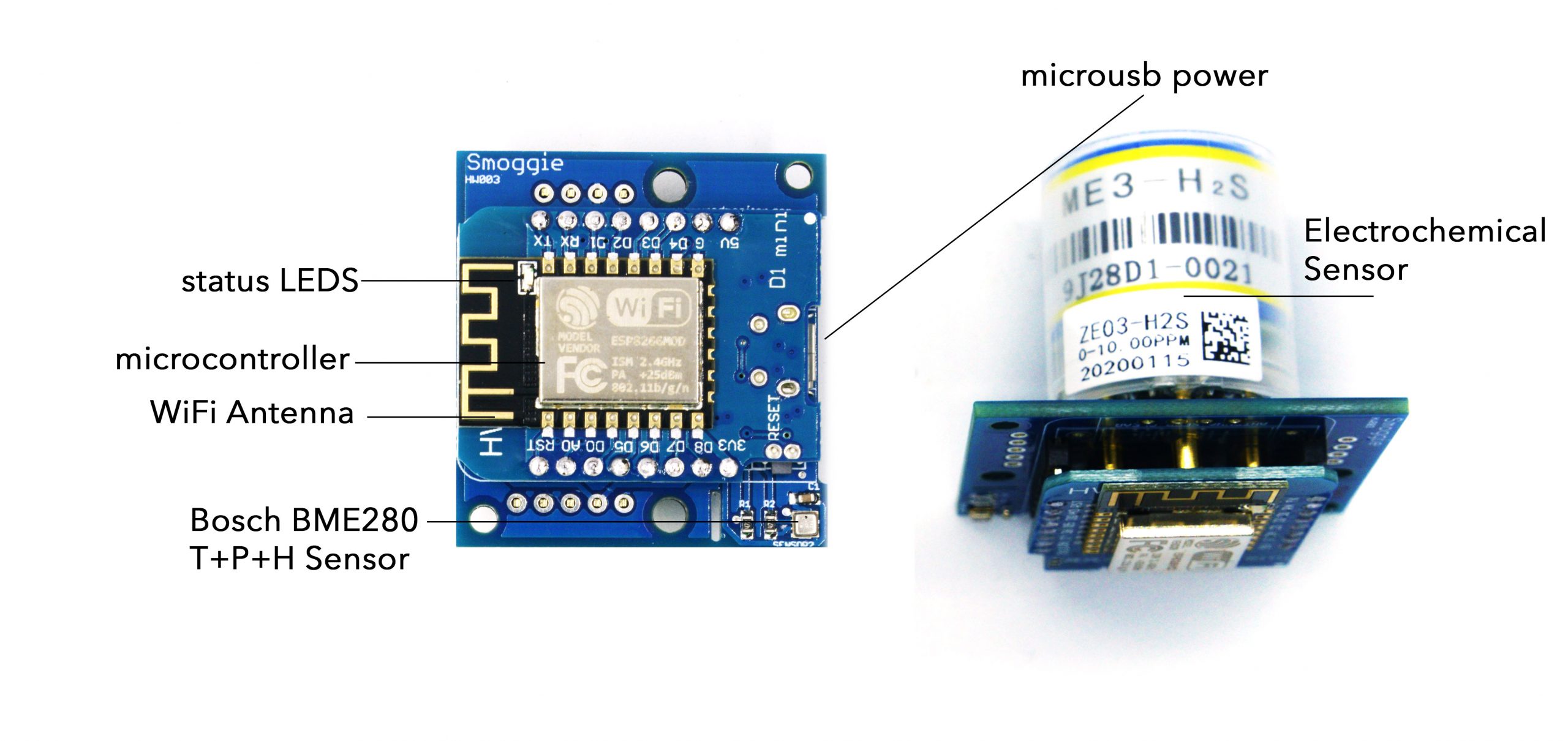
Picture: uRADMonitor SMOGGIE motherboard and enclosure
The units can be managed via the dashboard. The data can be viewed remotely on a computer or on a mobile device.

| Item | Parameter | Ratings |
| Voltage | External | 5V micro-USB |
| Consumption | Current | 80mA |
| Connectivity | Internet | Wifi |
| Microcontroller | ESP8266 | 8 bit |
| Enclosure | Rainproof plastic | 42x43x47 mm |
Your uRADMonitor unit can be mounted both indoors and outdoors where the enclosure offers protection against sun, rain or snow. The unit has a plastic enclosure with two holes and can be easily attached to a wall with only two screws. The sensor opening must face down for open air access. Make sure that nothing is blocking the air vents. The openings and the internal heating of the electronics are aligned to generate an active airflow.
Quick Setup
Connect it to power using a 5V micro-USB cable. Use a smartphone or a computer with WLAN capabilities to connect to the local hotspot spawned by your SMOGGIE unit. The SSID is uRADMonitor-XX, where XX are the last two digits of the Device ID number. The key is the Device ID, in uppercase, as printed on the enclosure. You can change this key later. Open 192.168.4.1 in your browser, and click the "WIFI/CONFIG" link to setup the connection to the Internet AP. Select the SSID and enter the key of your Internet Access Point.
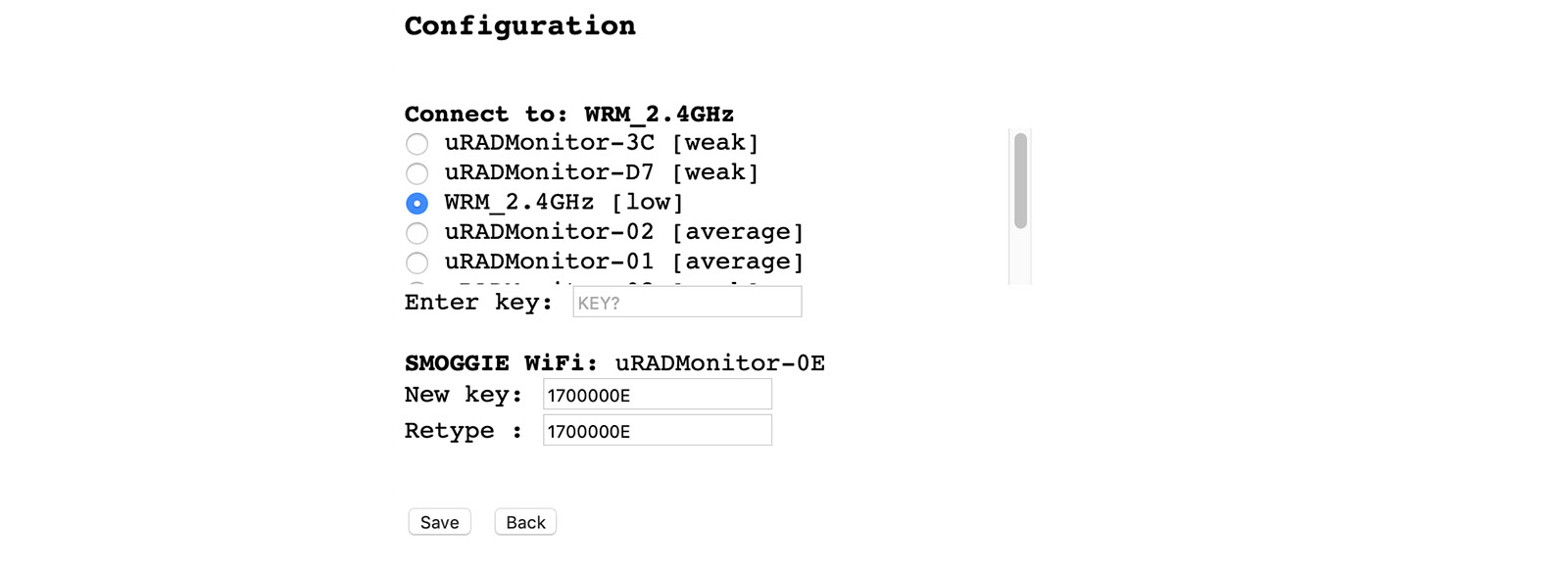
Picture: SMOGGIE Config Page
If the connection fails, you will see the status message.
USB configuration
Alternatively, the SSID and KEY can also be configured via USB. Connect to your SMOGGIE via USB, baudrate 9600bps, open a terminal program and type the two commands: "key1","SSID" then "key2","your WLAN key" . Use the "getsettings" command to verify that the new settings are in place. Quotes are a must, and there are no spaces in between. See the USB Commands manual for more. See the USB Commands manual if you need more help.
Quick Setup
Connect it to power using a 5V micro-USB cable. Use a smartphone or a computer with WLAN capabilities to connect to the local hotspot spawned by your SMOGGIE unit. The SSID is uRADMonitor-XX, where XX are the last two digits of the Device ID number. The key is the Device ID, in uppercase, as printed on the enclosure. You can change this key later. Open 192.168.4.1 in your browser, and click the "WIFI/CONFIG" link to setup the connection to the Internet AP. Select the SSID and enter the key of your Internet Access Point.

USB configuration
Alternatively, the SSID and KEY can also be configured via USB. Connect to your SMOGGIE via USB, baudrate 9600bps, open a terminal program and type the two commands: "key1","SSID" then "key2","your WLAN key" . Use the "getsettings" command to verify that the new settings are in place. Quotes are a must, and there are no spaces in between. See the USB Commands manual for more. See the USB Commands manual if you need more help.
Quick Start
Technical Datasheet
USB Serial Commands Manual
Product Limited Warranty terms
uRADMonitor with WIFI Configuration manual
Open source on Github
Data access:
Terms of Service
API Terms of Service
API and Server Specs
Direct Data access
USB Driver
In their recent versions, Windows, Linux and MacOS come with built in drivers for your uRADMonitor unit. Use the following resources only if the built in drivers do not work for you.
USB Driver for Windows
USB Driver for Linux
USB Driver for MacOS
RO:
RO: Ghid rapid de utilizare
RO: conditii generale de utilizare
Technical Datasheet
USB Serial Commands Manual
Product Limited Warranty terms
uRADMonitor with WIFI Configuration manual
Open source on Github
Data access:
Terms of Service
API Terms of Service
API and Server Specs
Direct Data access
USB Driver
In their recent versions, Windows, Linux and MacOS come with built in drivers for your uRADMonitor unit. Use the following resources only if the built in drivers do not work for you.
USB Driver for Windows
USB Driver for Linux
USB Driver for MacOS
RO:
RO: Ghid rapid de utilizare
RO: conditii generale de utilizare
SENSIGASContact us
The sensitivity of this sensor is unmatched: With this automated sensor you can monitor the gas you choose down to 1PPB resolution, so this will pick up even the gas traces in ambient air composition. It accommodates a single electrochemical cell that you can choose to match the gas you need to detect. Currently we support H2S, CO, NO2, SO2 and O3. There is an additional embedded sensor for temperature and humidity. It connects to the internet via WIFI and can be powered by a standard 5V micro-usb cable. It provides real time 24/7 monitoring for toxic gases.
Jacek, Poland: "These devices are impressive."
SENSIGAS is a high sensitivity automated sensor for toxic gases monitoring. It has Wifi connectivity to send the air quality measurements to the uRADMonitor Cloud in real time. It needs 5V to run, powered by a standard micro-USB cable. This unit doesn't have a screen, it works as a monitor and the data can be viewed remotely on a computer or on a mobile device.
To see complete specs see the technical datasheet.
By the nature of the technology used, any sensor can potentially fail to meet specification without warning. We make every effort to ensure reliability of all sensors but where life safety is a performance requirement of the product and, where practical, we recommend that all gas sensors and instruments using sensors are checked for response to gas before use. We accept no liability for any consequential losses, injury or damage resulting from the use of the uRADMonitor products. Customers should test the sensors under their own conditions to ensure that the sensors are suitable for their own requirements and in accordance with the plans and circumstances of the specified project and any standards / regulations pertaining to the country in which the sensors will be utilized.
| Sensor | Parameter | Resolution | Minimum value | Maximum value |
| MEMs | Temperature | 0.5°C | -40 °C | +85 °C |
| Humidity | 1%RH | 0%RH | 100% RH | |
| Electrochemical Sensor | H2S | 1 ppb | 1 ppb | 1 ppm |
| O3 | 1 ppb | 1 ppb | 1 ppm | |
| NO2 | 1 ppb | 1 ppb | 1 ppm | |
| SO2 | 1 ppb | 1 ppb | 1 ppm | |
| CO | 1 ppb | 1 ppb | 10 ppm |
By the nature of the technology used, any sensor can potentially fail to meet specification without warning. We make every effort to ensure reliability of all sensors but where life safety is a performance requirement of the product and, where practical, we recommend that all gas sensors and instruments using sensors are checked for response to gas before use. We accept no liability for any consequential losses, injury or damage resulting from the use of the uRADMonitor products. Customers should test the sensors under their own conditions to ensure that the sensors are suitable for their own requirements and in accordance with the plans and circumstances of the specified project and any standards / regulations pertaining to the country in which the sensors will be utilized.
Hydrogen sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula H2S. It is a colorless chalcogen hydride gas with the characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. It is very poisonous, corrosive, and flammable.
Hydrogen sulfide is often produced from the microbial breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen gas, such as in swamps and sewers; this process is commonly known as anaerobic digestion which is done by sulfate-reducing microorganisms. H2S also occurs in volcanic gases, natural gas, and in some sources of well water. [1]
Hydrogen sulfide is a broad-spectrum poison, meaning that it can poison several different systems in the body, although the nervous system is most affected. The toxicity of H2S is comparable with that of carbon monoxide. It binds with iron in the mitochondrial cytochrome enzymes, thus preventing cellular respiration. Since hydrogen sulfide occurs naturally in the body, the environment, and the gut, enzymes exist to detoxify it. At some threshold level, believed to average around 300–350 ppm, the oxidative enzymes become overwhelmed. Many personal safety gas detectors, such as those used by utility, sewage and petrochemical workers, are set to alarm at as low as 5 to 10 ppm and to go into high alarm at 15 ppm. Detoxification is effected by oxidation to sulfate, which is harmless. Hence, low levels of hydrogen sulfide may be tolerated indefinitely.
Exposure to lower concentrations can result in eye irritation, a sore throat and cough, nausea, shortness of breath, and fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema). These effects are believed to be due to the fact that hydrogen sulfide combines with alkali present in moist surface tissues to form sodium sulfide, a caustic. These symptoms usually go away in a few weeks.
Long-term, low-level exposure may result in fatigue, loss of appetite, headaches, irritability, poor memory, and dizziness. Chronic exposure to low level H2S (around 2 ppm) has been implicated in increased miscarriage and reproductive health issues among Russian and Finnish wood pulp workers, but the reports have not (as of circa 1995) been replicated.
Short-term, high-level exposure can induce immediate collapse, with loss of breathing and a high probability of death. If death does not occur, high exposure to hydrogen sulfide can lead to cortical pseudolaminar necrosis, degeneration of the basal ganglia and cerebral edema. Although respiratory paralysis may be immediate, it can also be delayed up to 72 hours.
0.00047 ppm or 0.47 ppb is the odor threshold, the point at which 50% of a human panel can detect the presence of an odor without being able to identify it.
10 ppm is the OSHA permissible exposure limit (PEL) (8 hour time-weighted average).
10–20 ppm is the borderline concentration for eye irritation.
20 ppm is the acceptable ceiling concentration established by OSHA.
50 ppm is the acceptable maximum peak above the ceiling concentration for an 8-hour shift, with a maximum duration of 10 minutes.
50–100 ppm leads to eye damage.
At 100–150 ppm the olfactory nerve is paralyzed after a few inhalations, and the sense of smell disappears, often together with awareness of danger.
320–530 ppm leads to pulmonary edema with the possibility of death.
530–1000 ppm causes strong stimulation of the central nervous system and rapid breathing, leading to loss of breathing.
800 ppm is the lethal concentration for 50% of humans for 5 minutes' exposure (LC50)
Concentrations over 1000 ppm cause immediate collapse with loss of breathing, even after inhalation of a single breath.
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. It is toxic to animals that use hemoglobin as an oxygen carrier (both Invertebrate and vertebrate) when encountered in concentrations above about 35 ppm, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal biological functions. In the atmosphere, it is spatially variable and short lived, having a role in the formation of ground-level ozone.[2] Carbon monoxide poisoning is the most common type of fatal air poisoning in many countries. Carbon monoxide is colorless, odorless, and tasteless, but highly toxic. It combines with hemoglobin to produce carboxyhemoglobin, which usurps the space in hemoglobin that normally carries oxygen, but is ineffective for delivering oxygen to bodily tissues. Concentrations as low as 667 ppm may cause up to 50% of the body's hemoglobin to convert to carboxyhemoglobin. A level of 50% carboxyhemoglobin may result in seizure, coma, and fatality. In the United States, the OSHA limits long-term workplace exposure levels above 50 ppm.
The most common symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning may resemble other types of poisonings and infections, including symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, fatigue, and a feeling of weakness. Affected families often believe they are victims of food poisoning. Infants may be irritable and feed poorly. Neurological signs include confusion, disorientation, visual disturbance, syncope (fainting), and seizures.
Some descriptions of carbon monoxide poisoning include retinal hemorrhages, and an abnormal cherry-red blood hue. In most clinical diagnoses these signs are seldom noticed. One difficulty with the usefulness of this cherry-red effect is that it corrects, or masks, what would otherwise be an unhealthy appearance, since the chief effect of removing deoxygenated hemoglobin is to make an asphyxiated person appear more normal, or a dead person appear more lifelike, similar to the effect of red colorants in embalming fluid. The "false" or unphysiologic red-coloring effect in anoxic CO-poisoned tissue is related to the meat-coloring commercial use of carbon monoxide, discussed below.
Carbon monoxide also binds to other molecules such as myoglobin and mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase. Exposures to carbon monoxide may cause significant damage to the heart and central nervous system, especially to the globus pallidus, often with long-term chronic pathological conditions. Carbon monoxide may have severe adverse effects on the fetus of a pregnant woman.
[1] Hydrogen sulfide
[2] Carbon monoxide
Hydrogen sulfide is often produced from the microbial breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen gas, such as in swamps and sewers; this process is commonly known as anaerobic digestion which is done by sulfate-reducing microorganisms. H2S also occurs in volcanic gases, natural gas, and in some sources of well water. [1]
Hydrogen sulfide is a broad-spectrum poison, meaning that it can poison several different systems in the body, although the nervous system is most affected. The toxicity of H2S is comparable with that of carbon monoxide. It binds with iron in the mitochondrial cytochrome enzymes, thus preventing cellular respiration. Since hydrogen sulfide occurs naturally in the body, the environment, and the gut, enzymes exist to detoxify it. At some threshold level, believed to average around 300–350 ppm, the oxidative enzymes become overwhelmed. Many personal safety gas detectors, such as those used by utility, sewage and petrochemical workers, are set to alarm at as low as 5 to 10 ppm and to go into high alarm at 15 ppm. Detoxification is effected by oxidation to sulfate, which is harmless. Hence, low levels of hydrogen sulfide may be tolerated indefinitely.
Exposure to lower concentrations can result in eye irritation, a sore throat and cough, nausea, shortness of breath, and fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema). These effects are believed to be due to the fact that hydrogen sulfide combines with alkali present in moist surface tissues to form sodium sulfide, a caustic. These symptoms usually go away in a few weeks.
Long-term, low-level exposure may result in fatigue, loss of appetite, headaches, irritability, poor memory, and dizziness. Chronic exposure to low level H2S (around 2 ppm) has been implicated in increased miscarriage and reproductive health issues among Russian and Finnish wood pulp workers, but the reports have not (as of circa 1995) been replicated.
Short-term, high-level exposure can induce immediate collapse, with loss of breathing and a high probability of death. If death does not occur, high exposure to hydrogen sulfide can lead to cortical pseudolaminar necrosis, degeneration of the basal ganglia and cerebral edema. Although respiratory paralysis may be immediate, it can also be delayed up to 72 hours.
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. It is toxic to animals that use hemoglobin as an oxygen carrier (both Invertebrate and vertebrate) when encountered in concentrations above about 35 ppm, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal biological functions. In the atmosphere, it is spatially variable and short lived, having a role in the formation of ground-level ozone.[2] Carbon monoxide poisoning is the most common type of fatal air poisoning in many countries. Carbon monoxide is colorless, odorless, and tasteless, but highly toxic. It combines with hemoglobin to produce carboxyhemoglobin, which usurps the space in hemoglobin that normally carries oxygen, but is ineffective for delivering oxygen to bodily tissues. Concentrations as low as 667 ppm may cause up to 50% of the body's hemoglobin to convert to carboxyhemoglobin. A level of 50% carboxyhemoglobin may result in seizure, coma, and fatality. In the United States, the OSHA limits long-term workplace exposure levels above 50 ppm.
The most common symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning may resemble other types of poisonings and infections, including symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, fatigue, and a feeling of weakness. Affected families often believe they are victims of food poisoning. Infants may be irritable and feed poorly. Neurological signs include confusion, disorientation, visual disturbance, syncope (fainting), and seizures.
Some descriptions of carbon monoxide poisoning include retinal hemorrhages, and an abnormal cherry-red blood hue. In most clinical diagnoses these signs are seldom noticed. One difficulty with the usefulness of this cherry-red effect is that it corrects, or masks, what would otherwise be an unhealthy appearance, since the chief effect of removing deoxygenated hemoglobin is to make an asphyxiated person appear more normal, or a dead person appear more lifelike, similar to the effect of red colorants in embalming fluid. The "false" or unphysiologic red-coloring effect in anoxic CO-poisoned tissue is related to the meat-coloring commercial use of carbon monoxide, discussed below.
Carbon monoxide also binds to other molecules such as myoglobin and mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase. Exposures to carbon monoxide may cause significant damage to the heart and central nervous system, especially to the globus pallidus, often with long-term chronic pathological conditions. Carbon monoxide may have severe adverse effects on the fetus of a pregnant woman.
[1] Hydrogen sulfide
[2] Carbon monoxide
SENSIGAS is designed to detect very low concentrations of toxic gases. It does this by using a high volume electrochemical sensor with enhanced stability and response. As an automated, fixed, Air Quality monitoring station that measures and reports the target gas concentration automatically, 24/7. It comes with built-in Wifi connectivity and it only needs 5V to run, supplied via a standard micro-USB cable. It will monitor your location 24/7 to inform you on elevated GAS levels that can impact your health. Each sensor comes with one electrochemical sensor to measure the gas you select at purchase time (H2S, O3, NO2, SO2 or CO). You can choose the gas at checkout.
The units can be managed via the dashboard. The data can be viewed remotely on a computer or on a mobile device.
The units can be managed via the dashboard. The data can be viewed remotely on a computer or on a mobile device.
| Item | Parameter | Ratings |
| Voltage | External | 5V micro-USB |
| Consumption | Current | 80mA |
| Connectivity | Internet | Wifi |
| Microcontroller | ESP8266 | 8 bit |
| Size and weight | Rainproof plastic | 57x44 (64 with brackets)x 60mm and 125grams |
Your uRADMonitor unit can be mounted both indoors and outdoors where the enclosure offers protection against sun, rain or snow. The unit has a plastic enclosure with two holes and can be easily attached to a wall with only two screws. The sensor opening must face down for open air access. Make sure that nothing is blocking the air vents. The openings and the internal heating of the electronics are aligned to generate an active airflow.
Quick Setup
Connect it to power using a 5V micro-USB cable. Use a smartphone or a computer with WLAN capabilities to connect to the local hotspot spawned by your SENSIGAS unit. The SSID is uRADMonitor-XX, where XX are the last two digits of the Device ID number. The key is the Device ID, in uppercase, as printed on the enclosure. You can change this key later. Open 192.168.4.1 in your browser, and click the "WIFI/CONFIG" link to setup the connection to the Internet AP. Select the SSID and enter the key of your Internet Access Point.

Picture: SENSIGAS Config Page
If the connection fails, you will see the status message.
USB configuration
Alternatively, the SSID and KEY can also be configured via USB. Connect to your SENSIGAS via USB, baudrate 9600bps, open a terminal program and type the two commands: "key1","SSID" then "key2","your WLAN key" . Use the "getsettings" command to verify that the new settings are in place. Quotes are a must, and there are no spaces in between. See the USB Commands manual for more. See the USB Commands manual if you need more help.
Quick Setup
Connect it to power using a 5V micro-USB cable. Use a smartphone or a computer with WLAN capabilities to connect to the local hotspot spawned by your SENSIGAS unit. The SSID is uRADMonitor-XX, where XX are the last two digits of the Device ID number. The key is the Device ID, in uppercase, as printed on the enclosure. You can change this key later. Open 192.168.4.1 in your browser, and click the "WIFI/CONFIG" link to setup the connection to the Internet AP. Select the SSID and enter the key of your Internet Access Point.

USB configuration
Alternatively, the SSID and KEY can also be configured via USB. Connect to your SENSIGAS via USB, baudrate 9600bps, open a terminal program and type the two commands: "key1","SSID" then "key2","your WLAN key" . Use the "getsettings" command to verify that the new settings are in place. Quotes are a must, and there are no spaces in between. See the USB Commands manual for more. See the USB Commands manual if you need more help.
Quick Start
Technical Datasheet
USB Serial Commands Manual
Product Limited Warranty terms
uRADMonitor with WIFI Configuration manual
Open source on Github
Data access:
Terms of Service
API Terms of Service
API and Server Specs
Direct Data access
USB Driver
In their recent versions, Windows, Linux and MacOS come with built in drivers for your uRADMonitor unit. Use the following resources only if the built in drivers do not work for you.
USB Driver for Windows
USB Driver for Linux
USB Driver for MacOS
RO:
RO: Ghid rapid de utilizare
RO: conditii generale de utilizare
Technical Datasheet
USB Serial Commands Manual
Product Limited Warranty terms
uRADMonitor with WIFI Configuration manual
Open source on Github
Data access:
Terms of Service
API Terms of Service
API and Server Specs
Direct Data access
USB Driver
In their recent versions, Windows, Linux and MacOS come with built in drivers for your uRADMonitor unit. Use the following resources only if the built in drivers do not work for you.
USB Driver for Windows
USB Driver for Linux
USB Driver for MacOS
RO:
RO: Ghid rapid de utilizare
RO: conditii generale de utilizare
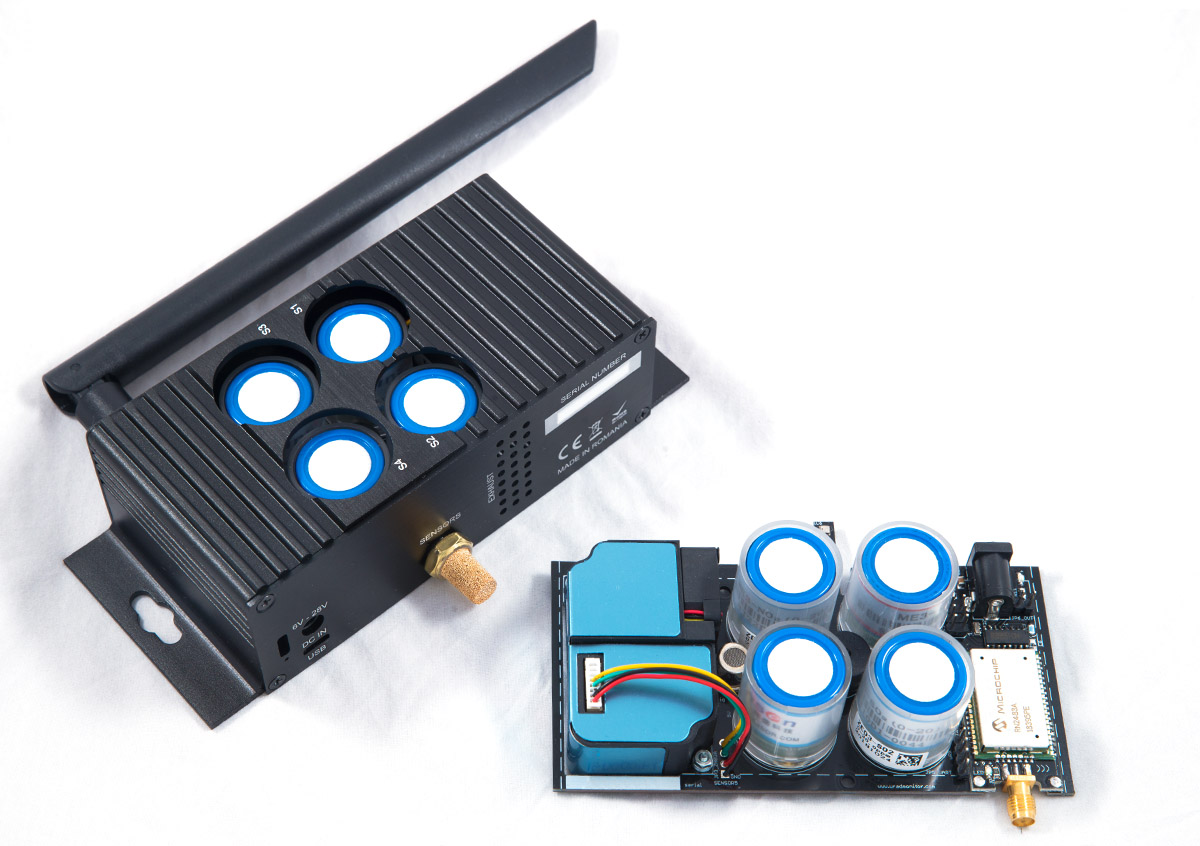

 Available, ships right away.
Available, ships right away.
